Tocilizumab vs Dexamethasone (RCT)
Hospitalized patients
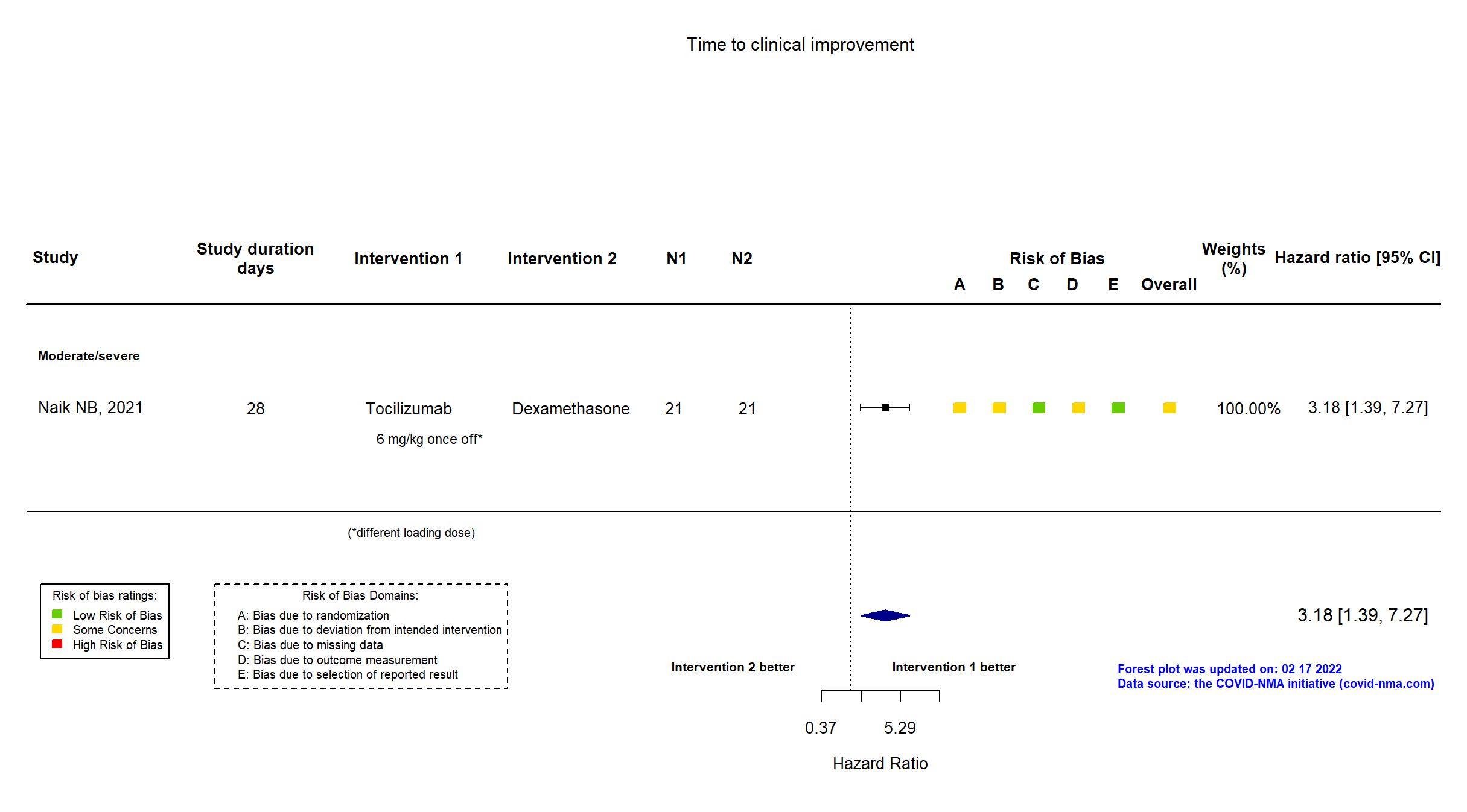
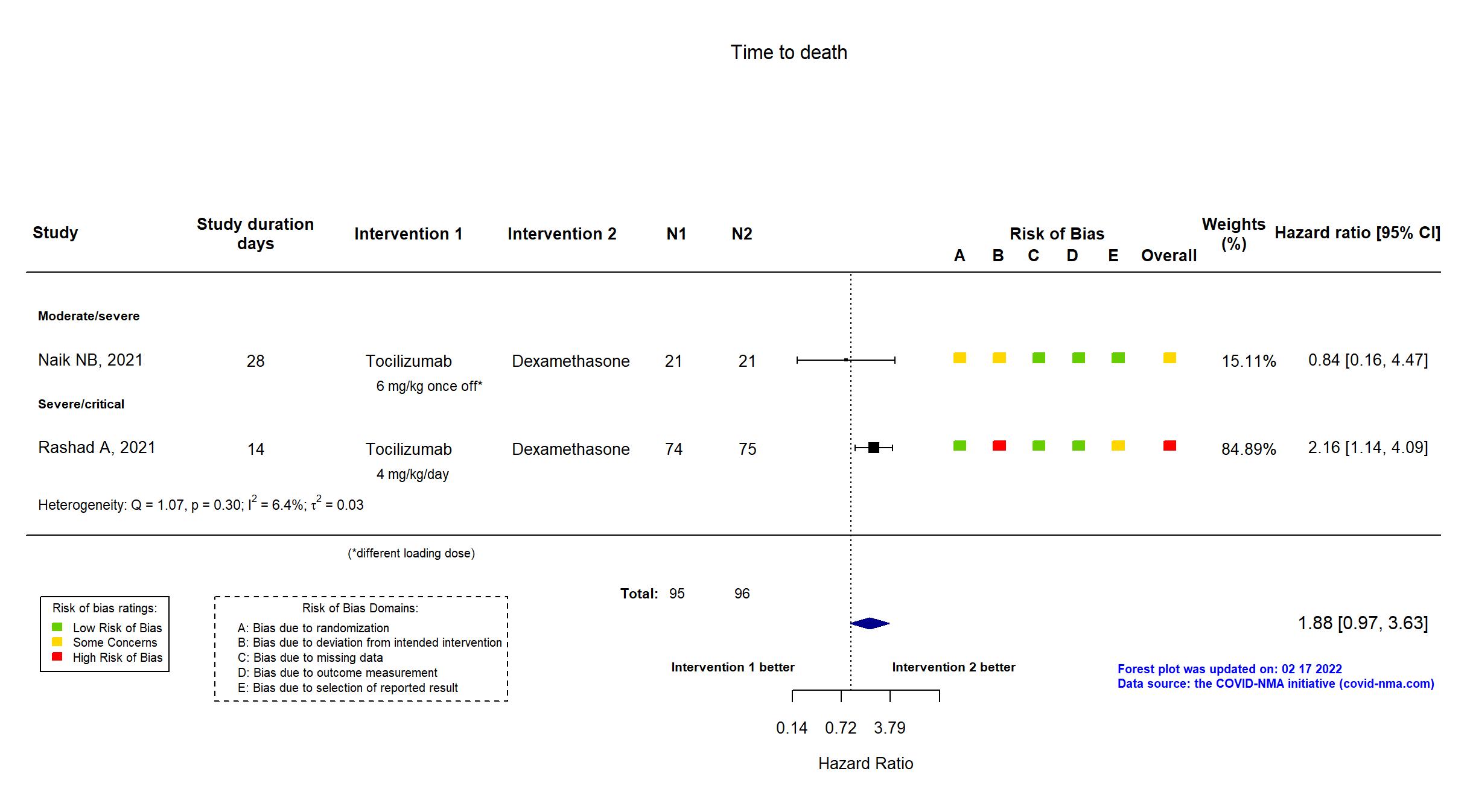
FOREST PLOTS -2022-02-17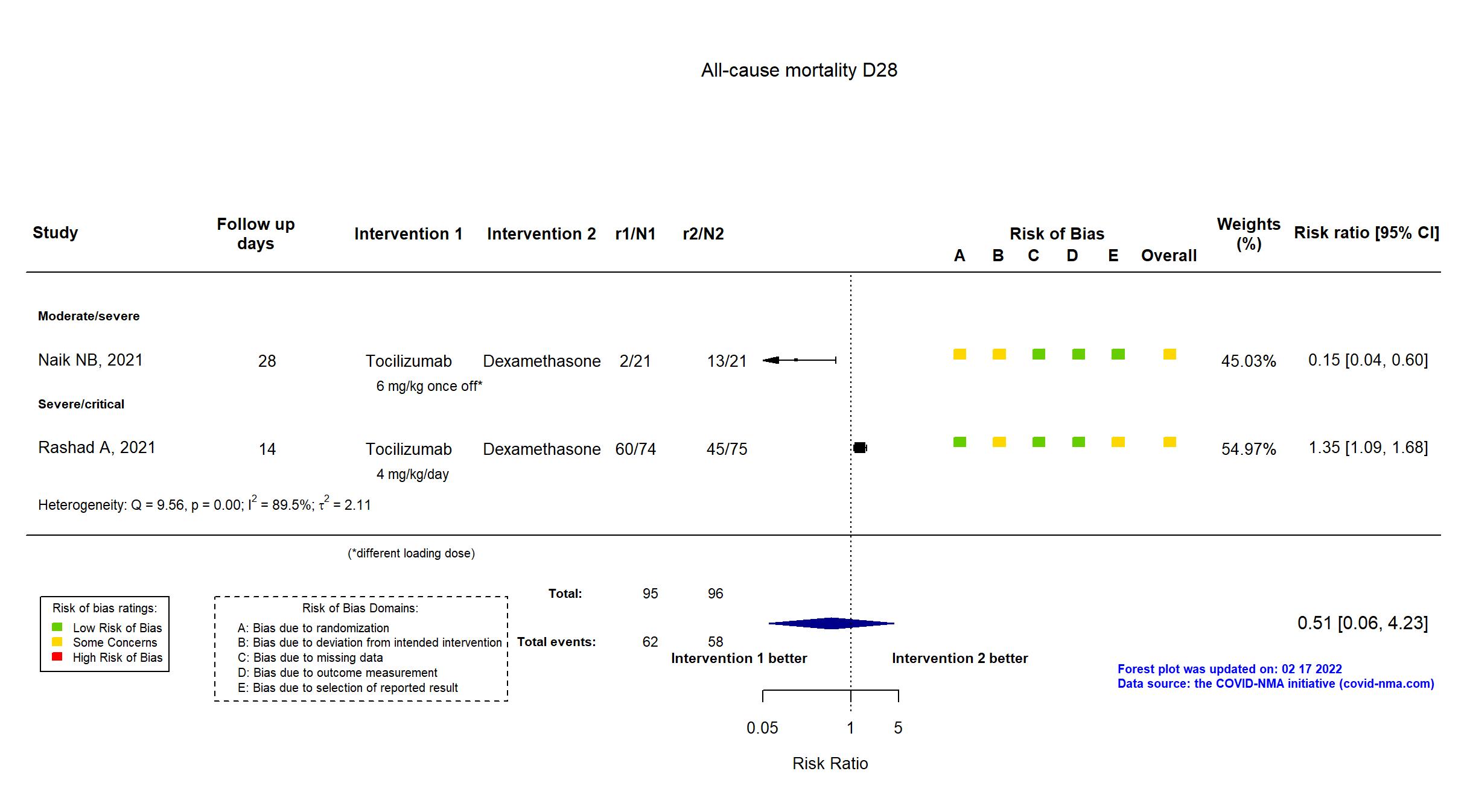



Trial CTRI/2021/04/033263
Publication Naik NB, Cureus (2021) (published paper)
Dates: 2021-05-06 to 2021-06-30
Funding: Public/non profit (Source of monetary of material support - Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education and Research)
Conflict of interest: *
| Methods | |
| RCT Blinding: Unblinded | |
| Location :
Single center / India Follow-up duration (days): 28 | |
| Inclusion criteria |
|
| Exclusion criteria |
|
| Interventions | |
| Treatment
Tocilizumab 6 mg/kg intravenously once-off. An additional similar dose after 24 hours if no clinical improvement. |
|
| Control
Dexamethasone 20 mg intravenously once daily for 3 days | |
| Participants | |
| Randomized participants : Dexamethasone=21 Tocilizumab=21 | |
| Characteristics of participants N= 42 Mean age : NR 24 males Severity : Mild: n=0 / Moderate: n=36 / Severe: n=6 Critical: n=0 | |
| Primary outcome | |
| In the register Ventilator free days (VFD) Timepoint: 0-28days following admission. | |
| In the report Ventilator-free days (VFDs) within 28 days since randomization. | |
| Documents avalaible |
Protocol NR Statistical plan NR Data-sharing willing stated in the publication: Not reported |
| Risk of bias Overall The overall risk of bias reported in the table corresponds to the highest risk of bias for the outcomes assessed for the systematic review |
Some concerns |
| General comment | In addition to the published article, the trial registry and supplementary appendices were used in data extraction and assessment of risk of bias. Only graphical summaries of the protocol and statistical analysis plan were available. The study was terminated at the interim analysis stage due to increased mortality and adverse event rate observed in the high dose dexamethasone arm and therefore did not achieve the target sample size (n=42 of planned n=102). The primary outcome indicated in registry reflects the primary outcome reported in the paper. There is no change from the trial registration in the intervention and control treatments. |
Trial NCT04519385
Publication Rashad A, Scientific Reports (2021) (published paper)
Dates: 2020-03-01 to 2020-06-30
Funding: Not reported/unclear (Open access funding: Qatar National Library)
Conflict of interest: No
| Methods | |
| RCT Blinding: Unblinded | |
| Location :
Single center / Egypt Follow-up duration (days): 14 | |
| Inclusion criteria |
|
| Exclusion criteria |
|
| Interventions | |
| Treatment
Tocilizumab 4 mg/kg IV once daily for two days |
|
| Control
Dexamethasone Initial dose: 4 mg/kg IV once daily for 3 days, Maintenance dose: 8 mg once daily for ten days | |
| Participants | |
| Randomized participants : Tocilizumab=74 Dexamethasone=75 | |
| Characteristics of participants N= 149 Mean age : NR 62 males Severity : Mild: n=0 / Moderate: n=0 / Severe: n=70 Critical: n=39 | |
| Primary outcome | |
| In the register Proportion of participants with Overall Survival at 14 days | |
| In the report Time to failure, defined as death, within 14 days from ICU admission | |
| Documents avalaible |
Protocol NR Statistical plan NR Data-sharing willing stated in the publication: Yes |
| Risk of bias Overall The overall risk of bias reported in the table corresponds to the highest risk of bias for the outcomes assessed for the systematic review |
High |
| General comment | In addition to the published article, the retrospective study registry was used in data extraction and risk of bias assessment. Neither protocol nor statistical analysis plan was available. Blinding is unclear: the report states that “Patients, investigators, and health-care providers were not masked to study drug assignment”; despite being retrospectively registered, the trial is described as single-blind in the registry, with participants and outcome assessor blinded. Described in the report as taking place “in the ICU of ESNA hospital, the first COVID-19 quarantine hospital in Egypt”; yet randomization described as being “stratified by site”. The secondary outcome included in the registry (Fio2/Pao2, Time Frame: 2 days) is not reported as an outcome, but rather considered as a predictor for survival. The study excluded all deaths within the first 3 days (38% vs. 16% of participants in the two groups) from mortality analyses and was consequently assessed as high risk of bias. |