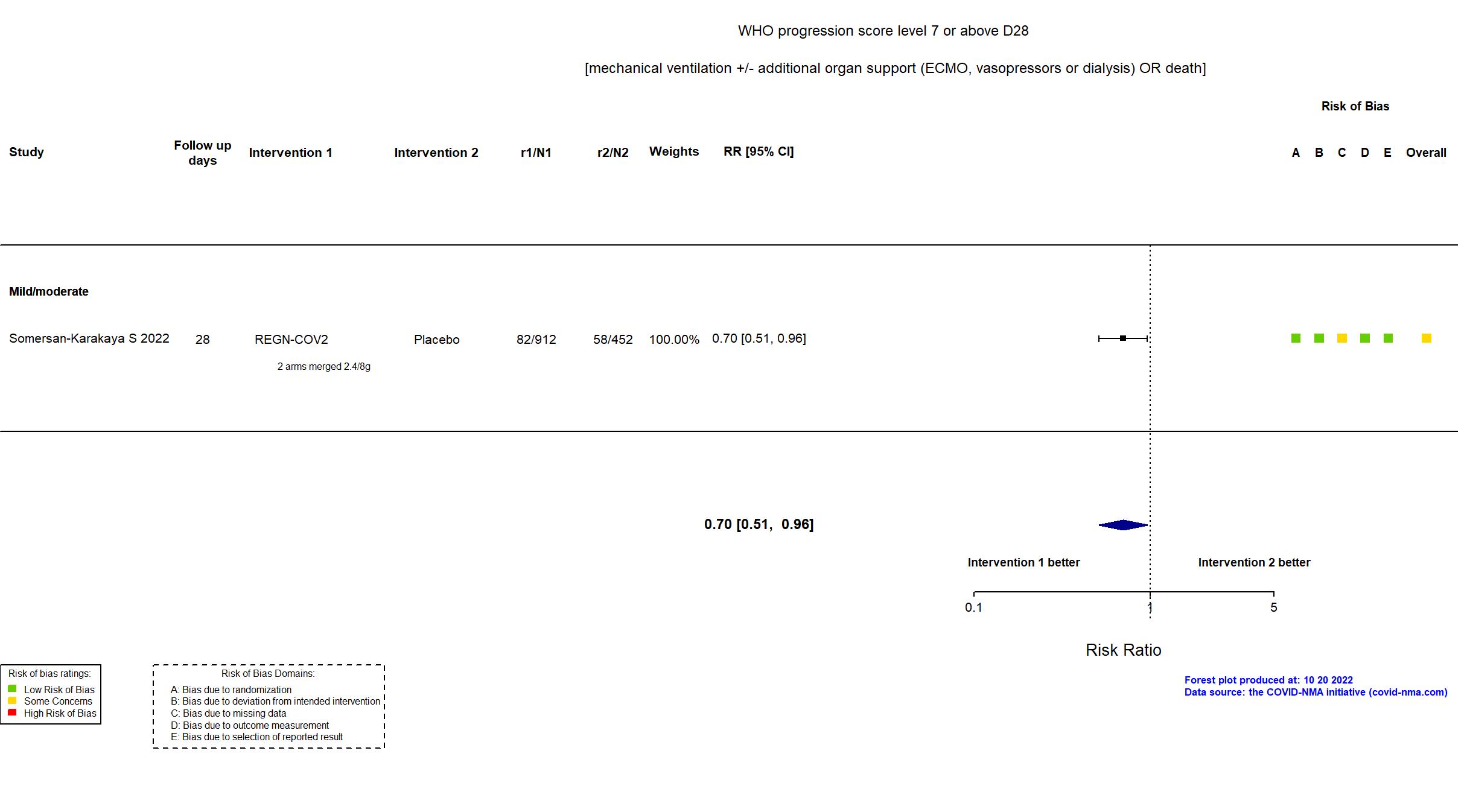
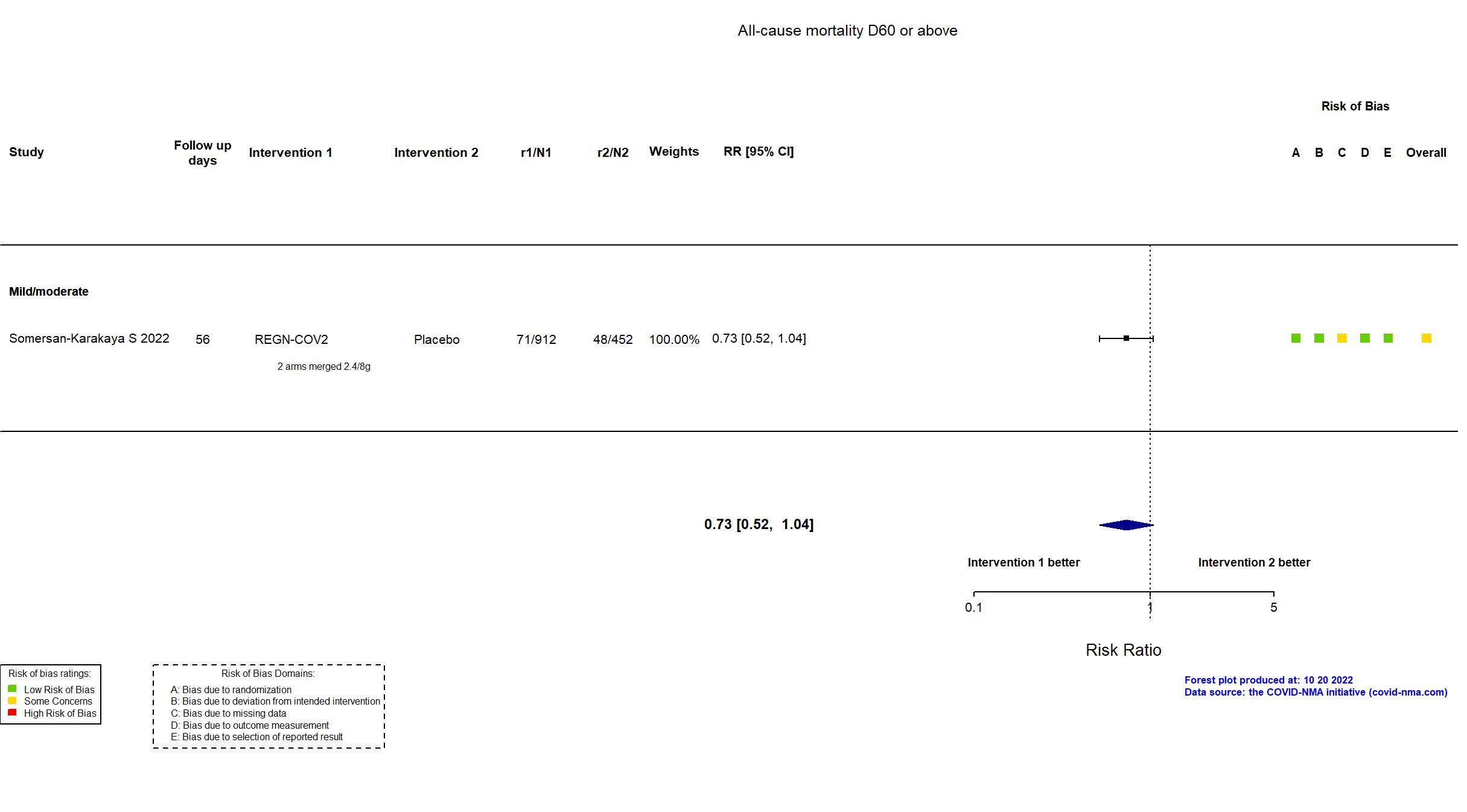
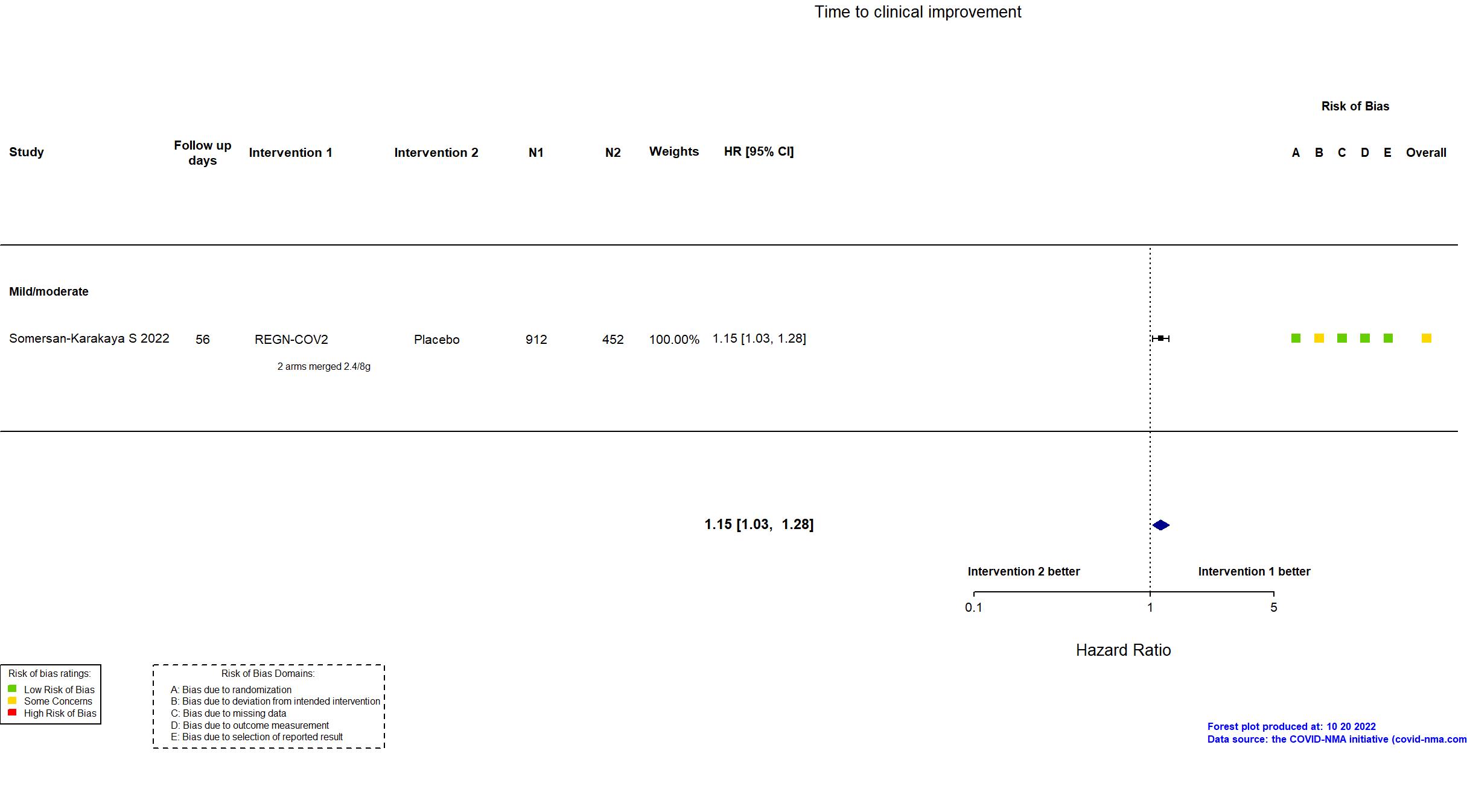
Casirivimab+Imdevimab (REGN-COV2) vs Standard care/Placebo (RCT)
Hospitalized patients
FOREST PLOTS -2022-10-20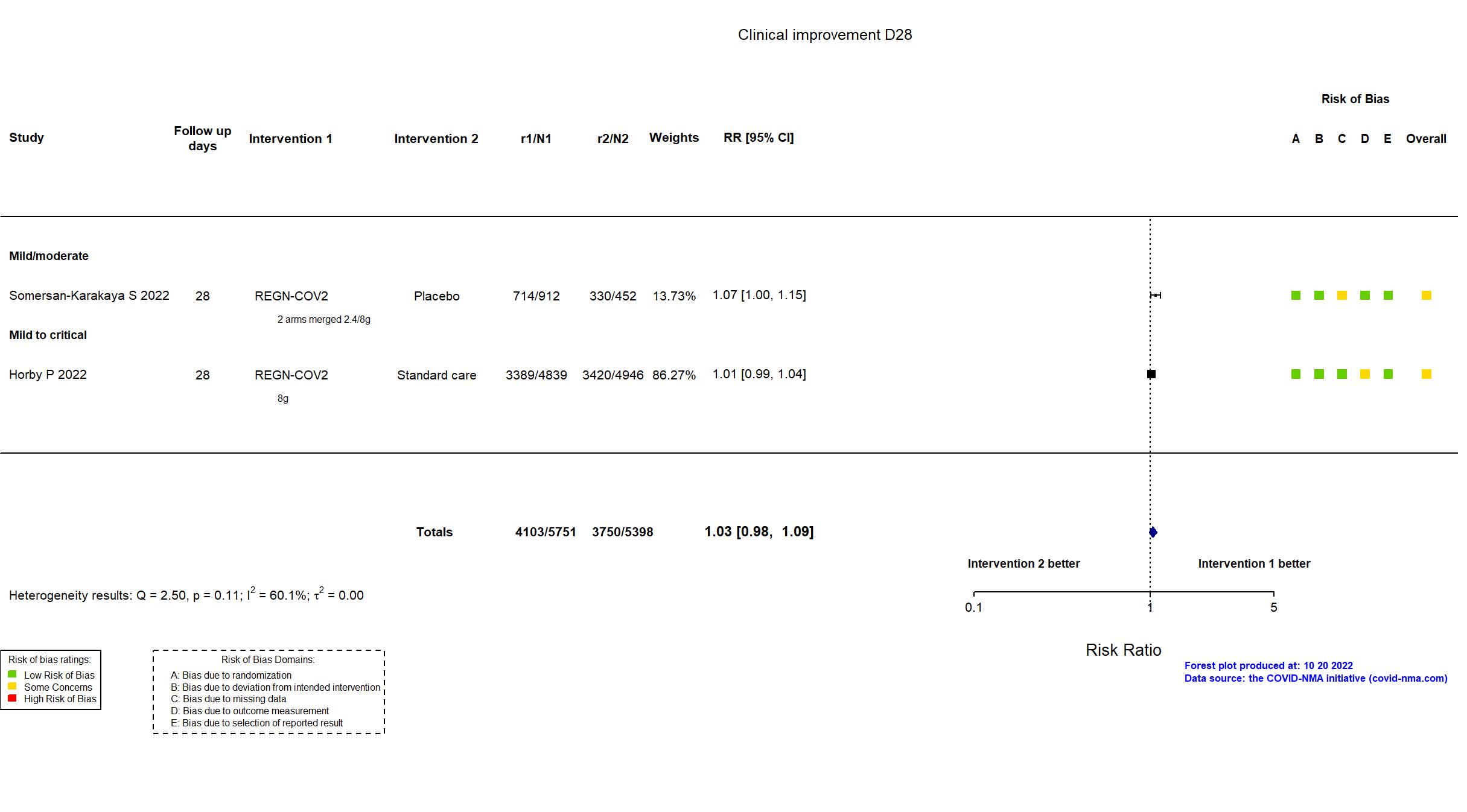










Trial NCT04381936, EudraCT 2020-001113-21, ISRCTN5018967
Publication RECOVERY-REGEN - Horby P, Lancet (2022) (published paper)
Dates: 2020-09-18 to 2021-05-22
Funding: Mixed (UK Research and Innovation (Medical Research Council); National Institute of Health Research; Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc. (REGEN-COV2 donation))
Conflict of interest: Yes
| Methods | |
| RCT Blinding: Unblinded | |
| Location :
Multicenter / UK Follow-up duration (days): 28 | |
| Inclusion criteria |
|
| Exclusion criteria |
|
| Interventions | |
| Treatment
REGN-COV2 8g (casirivimab 4g and imdevimab 4g) in 250ml 0.9% saline intravenously over 60 minutes +/- 15 minutes |
|
| Control
Standard care | |
| Participants | |
| Randomized participants : REGN-COV2=4839 Standard care=4946 | |
| Characteristics of participants N= 9785 Mean age : NR 6128 males Severity : Mild: n=641 / Moderate: n=5996 / Severe: n=2561 Critical: n=587 | |
| Primary outcome | |
| In the register All-cause mortality [ Time Frame: Within 28 days after randomisation ] | |
| In the report 28-day all-cause mortality | |
| Documents avalaible |
Protocol Yes. In English Statistical plan Yes Data-sharing willing stated in the publication: Yes |
| Risk of bias Overall The overall risk of bias reported in the table corresponds to the highest risk of bias for the outcomes assessed for the systematic review |
Some concerns |
| General comment |
The RECOVERY trial is an investigator-initiated, individually randomized, controlled, open-label, adaptive platform trial to evaluate the effects of potential treatments in patients hospitalized with COVID-19. The trial is underway at 177 hospitals in the United Kingdom two hospitals in Indonesia, and two hospitals in Nepal. 127 UK hospitals took part in the evaluation of REGEN-COV. In addition to the published article, the pre-print article, protocol, statistical analysis plan, and prospective registries (NCT04381936 May 11 2020, EudraCT 2020-001113-21 March 19 2020, ISRCTN50189673 April 2 2020) were used in data extraction and assessment of risk of bias. There were no substantive differences between the protocol and trial registries in population, procedures, interventions or outcomes. Information on the primary outcome was available for 99% of randomised patients for this preliminary analysis; patients who had not been followed for 28 days and were not known to have died by the time of the data cut (25 May 2021) were not included. No target sample size was pre-specified. On 27 April 2021, the trial steering committee, unaware of the results of the trial comparisons, determined that, with over 9700 patients recruited to the REGEN-COV comparison, further recruitment was unlikely to increase reliability of the results materially and recruitment was terminated.
The study was updated on the March 1st, 2022 with data from the published report. |
Trial NCT04426695
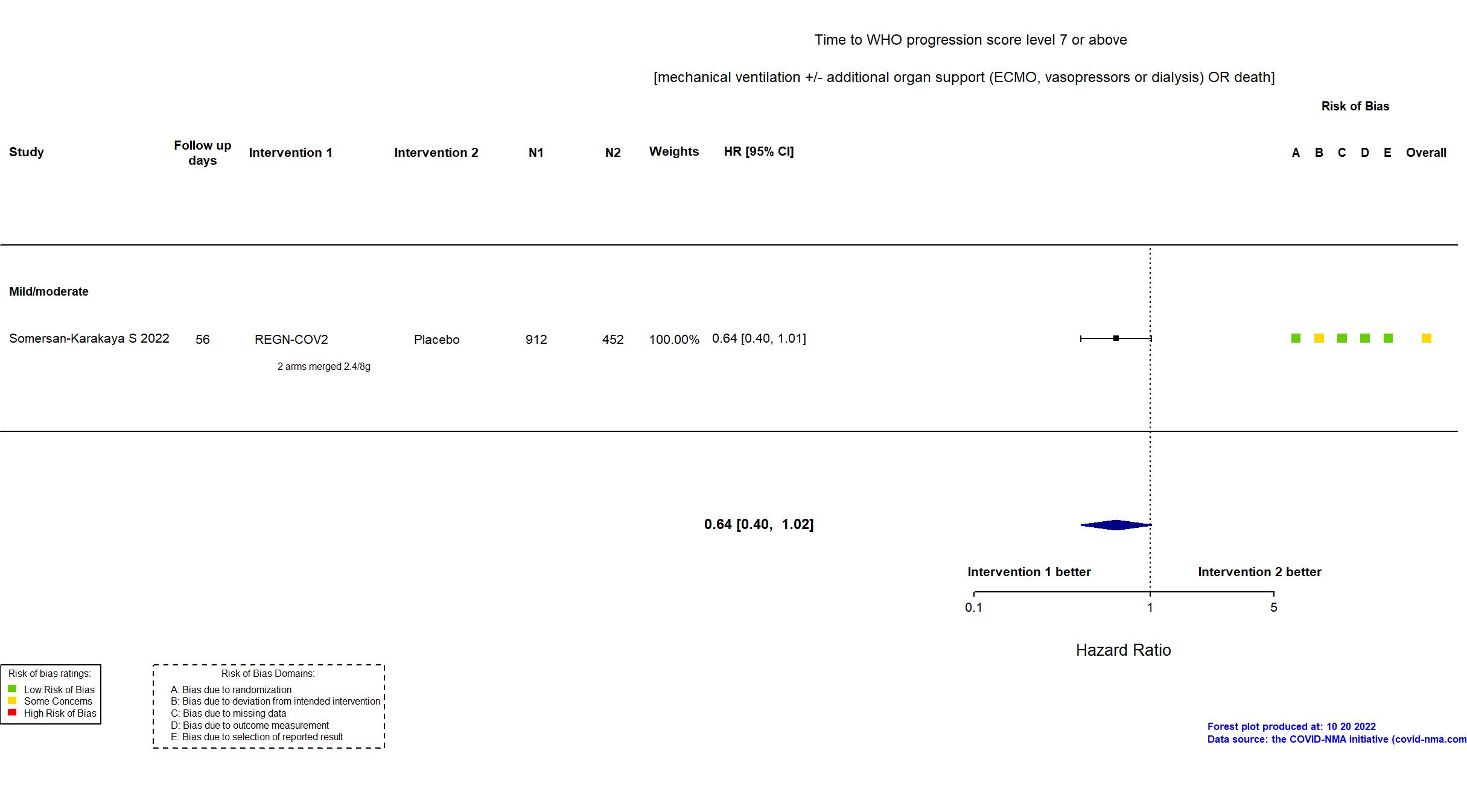
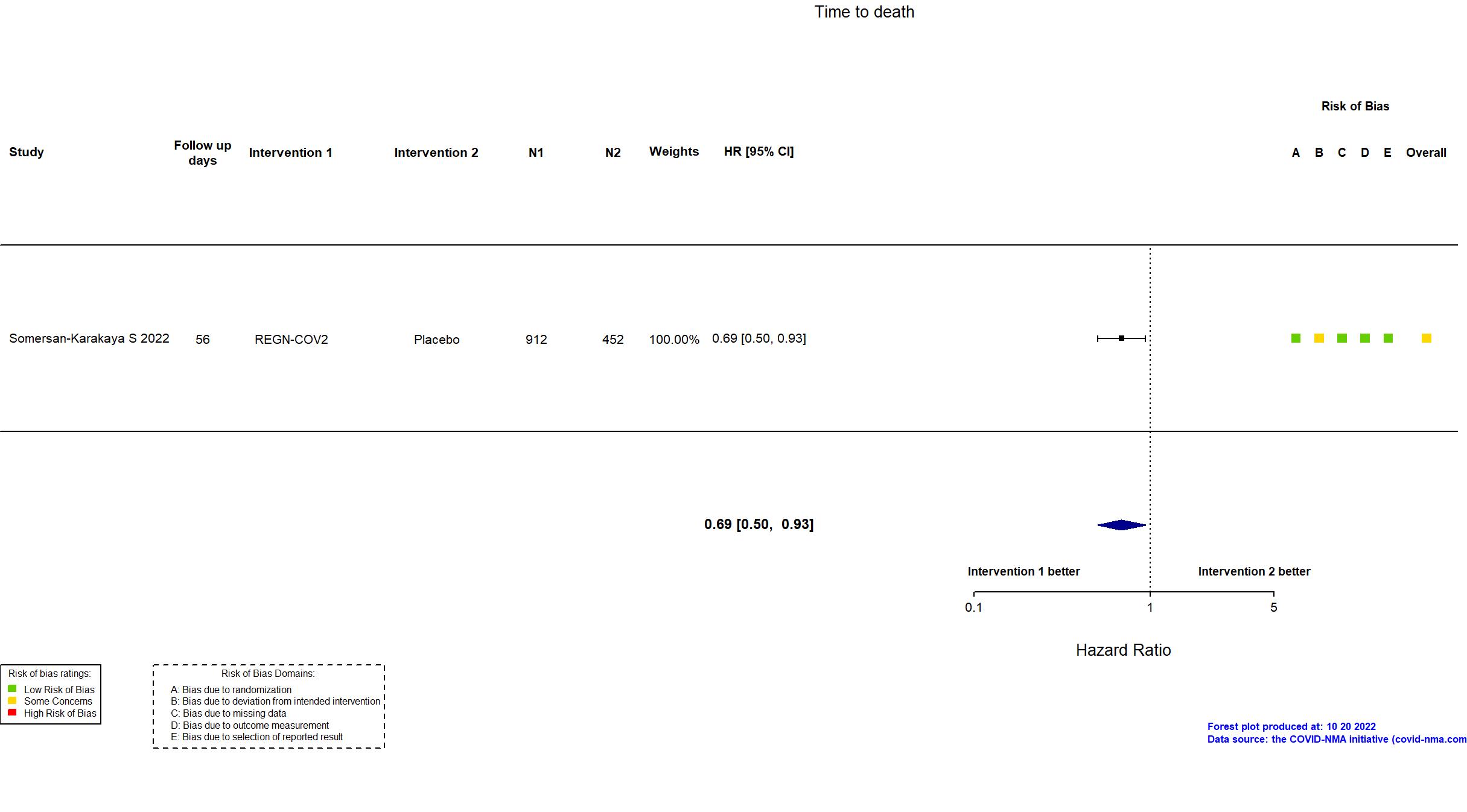
Publication Somersan-Karakaya S, J Infect Dis (2022) (published paper)
Dates: 2020-06-11 to 2021-04-09
Funding: Mixed (Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; Department of Health and Human Services; Office of the Assistant Secretary for Preparedness and Response; Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority.)
Conflict of interest: Yes
| Methods | |
| RCT Blinding: double blinding | |
| Location :
Multicenter / USA, Brazil, Chile, Mexico, Moldova, Romania Follow-up duration (days): 56 | |
| Inclusion criteria |
|
| Exclusion criteria |
|
| Interventions | |
| Treatment
REGN-COV2 2400mg 1200 mg Casirivimab and 1200 mg Imdevimab intravenously single dose REGN-COV2 8000mg 4000 mg Casirivimab and 4000 mg Imdevimab intravenously single dose REGN-COV2 4000 mg Casirivimab and 4000 mg Imdevimab intravenously single dose |
|
| Control
Placebo | |
| Participants | |
| Randomized participants : Placebo=452 REGN-COV2 2400mg=457 REGN-COV2 8000mg=455 REGN-COV2=912 | |
| Characteristics of participants N= 2276 Mean age : NR 863 males Severity : Mild: n=700 / Moderate: n=894 / Severe: n=1 Critical: n=0 | |
| Primary outcome | |
| In the register 1) Time-weighted average change from baseline in viral load as measured by quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) in nasopharyngeal (NP) swab samples [ Time Frame: Baseline to Day 7 ]; 2) Proportion of patients who died or required mechanical ventilation [ Time Frame: Day 6 through Day 29 ]; 3) Proportion of patients who died or required mechanical ventilation [ Time Frame: Day 1 through Day 29 ]; 4) Incidence of patients who died or required mechanical ventilation [ Time Frame: Up to day 29 ]; 5) Proportion of patients with treatment-emergent Serious Adverse Events (SAEs) [ Time Frame: Through Day 169 ] 6) Proportion of patients with infusion-related reactions [ Time Frame: Through Day 4 ]; 7) Proportion of patients with hypersensitivity reactions [ Time Frame: Through Day 29 ] | |
| In the report 1) Primary virologic efficacy endpoint - time-weighted average (TWA) daily change from baseline (day 1) viral load in nasopharyngeal samples through day 7; 2) Primary clinical efficacy endpoint - proportion of patients who died or required mechanical ventilation from day 6-29 and day 1-29. | |
| Documents avalaible |
Protocol Yes. In English Statistical plan Yes Data-sharing willing stated in the publication: Yes |
| Risk of bias Overall The overall risk of bias reported in the table corresponds to the highest risk of bias for the outcomes assessed for the systematic review |
Some concerns |
| General comment |
In addition to all versions of the pre-print article, the prospective trial registry, protocol (obtained from contact with authors), and supplementary appendices were used in data extraction and assessment of risk of bias. Neither protocol nor statistical analysis plan was available. Only three of seven primary outcomes in the registry are described as primary outcomes in the article. Otherwise, there were no important differences between the registry and the article. The trial was terminated early due to slow recruitment and did not achieve its target sample size.
This study was updated on the March 2nd, 2022 with data extracted from the fourth version of the preprint. This study was updated on the May 9th, 2022 with data obtained from contact with authors. This study was further updated on September 1st, 2022 after publication of the study report. |