Bamlanivimab vs Placebo (RCT)
Hospitalized patients
FOREST PLOTS -2022-10-07
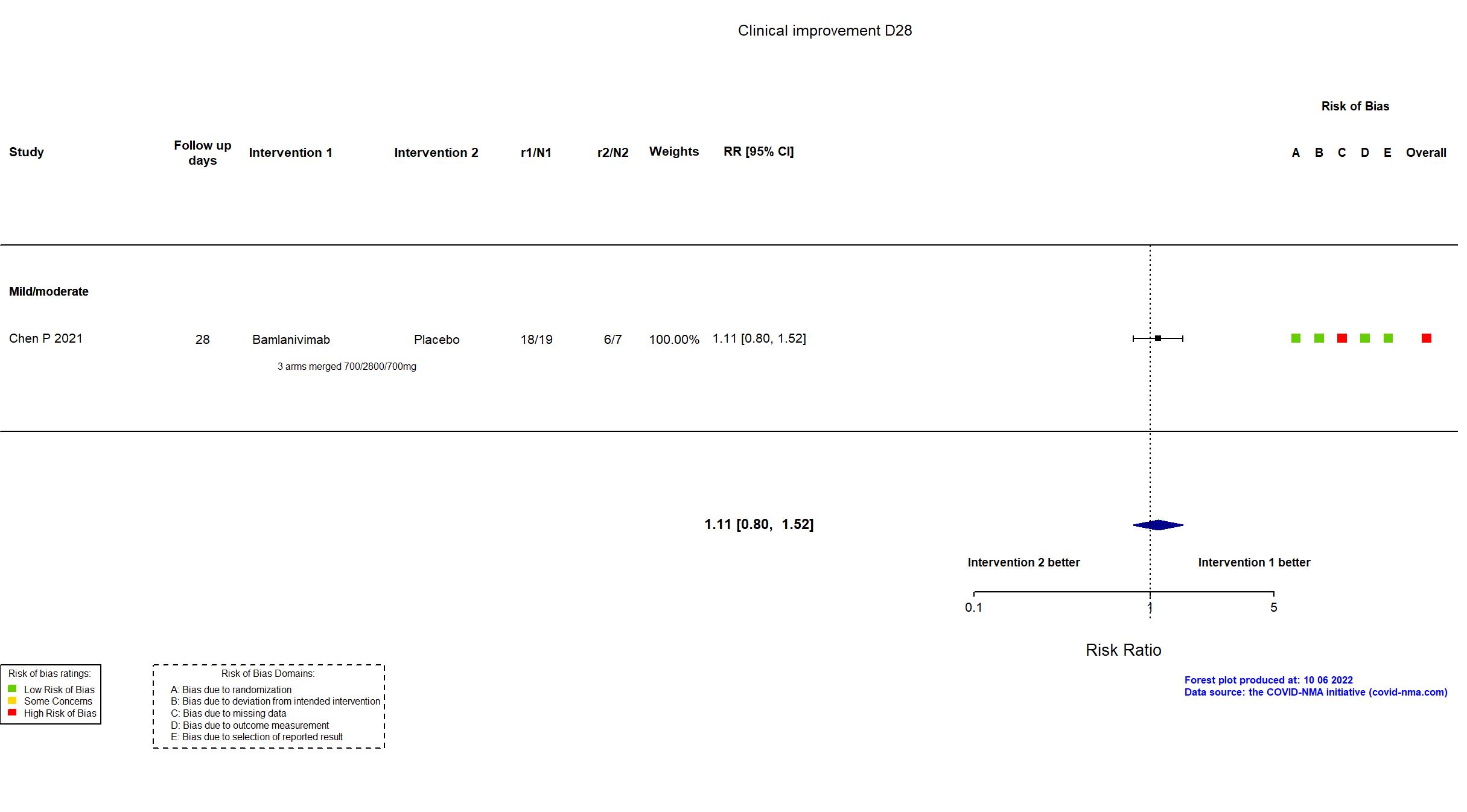

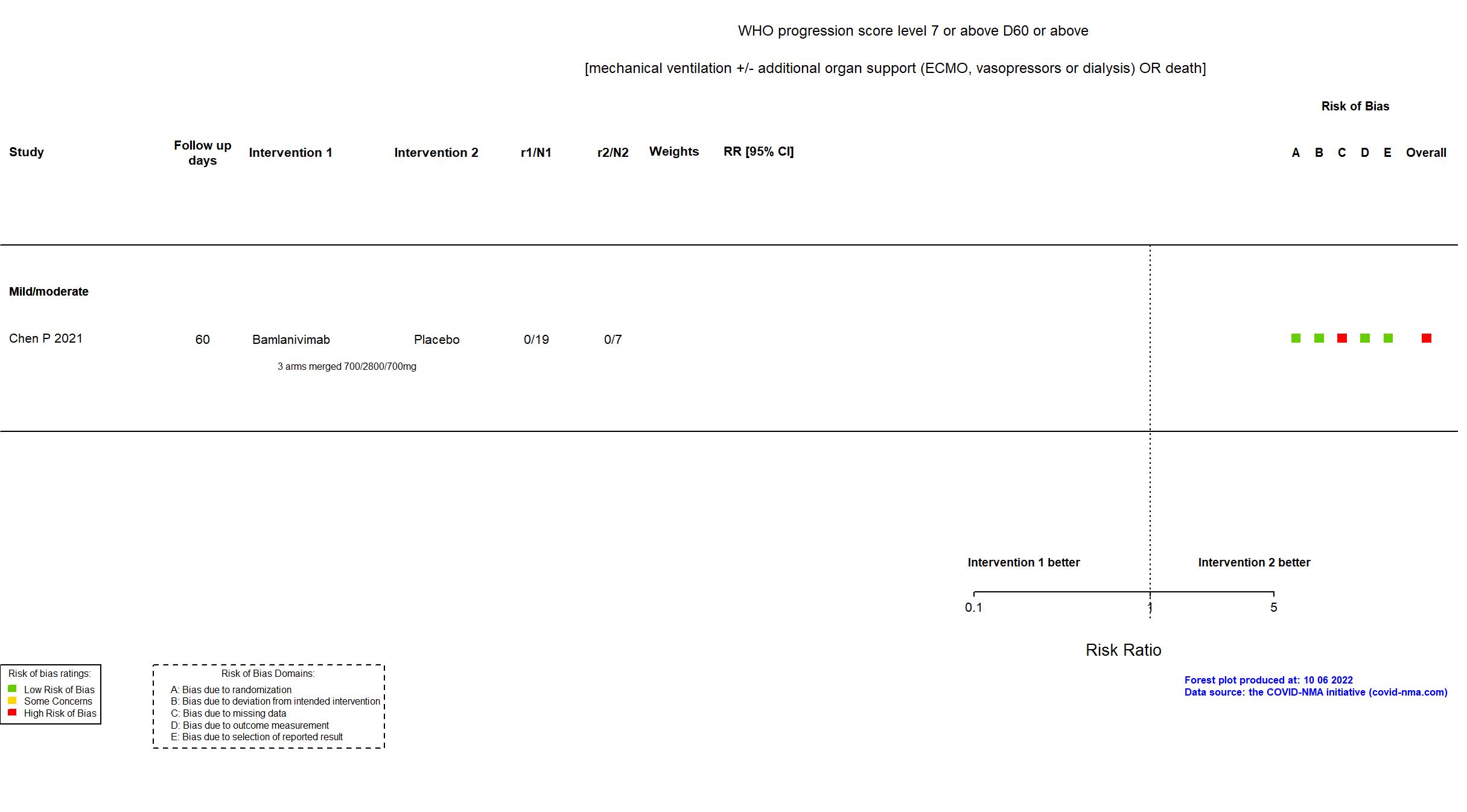
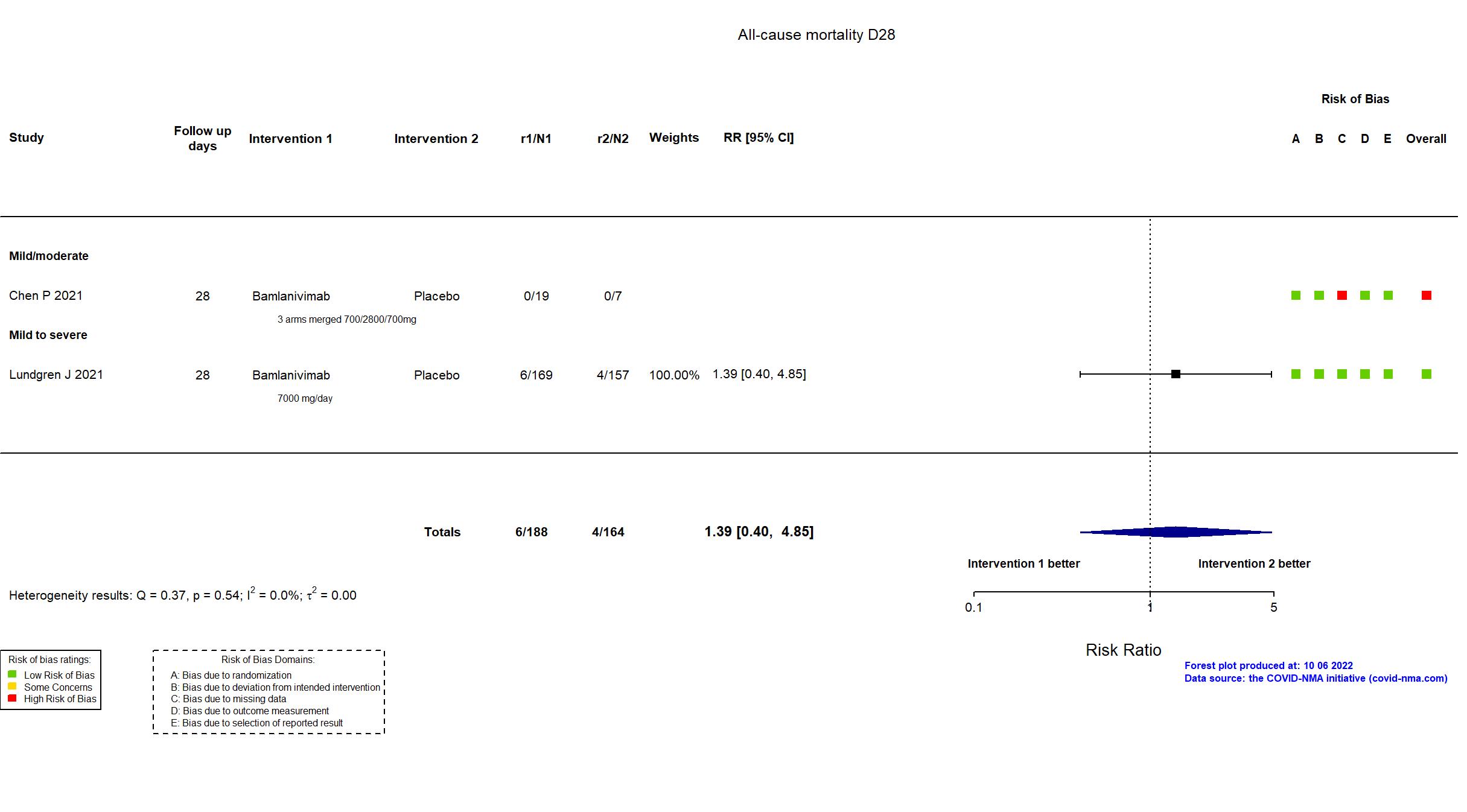
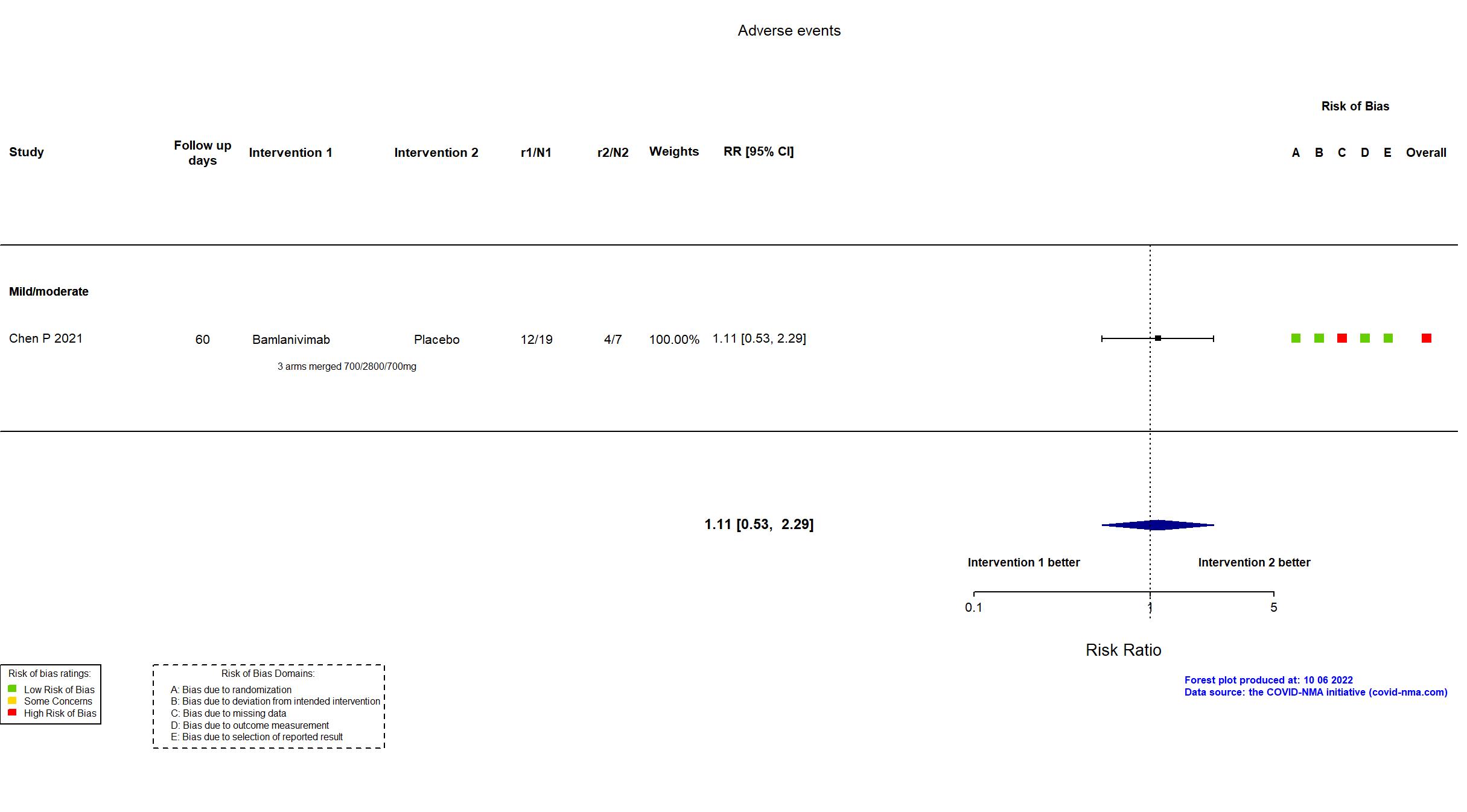










Trial NCT04411628
Publication J2W-MC-PYAA - Chen P, Clin Pharmacol Ther (2021) (published paper)
Dates: 2020-05-29 to 2020-06-28
Funding: Private (Eli Lilly and Company)
Conflict of interest: Yes
| Methods | |
| RCT Blinding: triple blinding | |
| Location :
Multicenter / USA Follow-up duration (days): 60 | |
| Inclusion criteria |
|
| Exclusion criteria |
|
| Interventions | |
| Treatment
Bamlanivimab 700 mg 700 mg (50 mL) administered intravenously at 100 mL/hr for 30 minutes on Day 1 Bamlanivimab 2800 mg 2800 mg (75 mL) administered intravenously at 100 mL/hr for 45 minutes on Day 1 Bamlanivimab 7000 mg 7000 mg (50 mL) administered intravenously at 100 mL/hr for 60 minutes on Day 1 Bamlanivimab 700 mg (50 mL) administered intravenously at 100 mL/hr for 30 minutes on Day 1 |
|
| Control
Placebo | |
| Participants | |
| Randomized participants : Bamlanivimab 700 mg =6 Bamlanivimab 2800 mg =7 Bamlanivimab 7000 mg=6 Placebo=7 Bamlanivimab=19 | |
| Characteristics of participants N= 45 Mean age : NR 17 males Severity : Mild: n=10 / Moderate: n=20 / Severe: n=0 Critical: n=0 | |
| Primary outcome | |
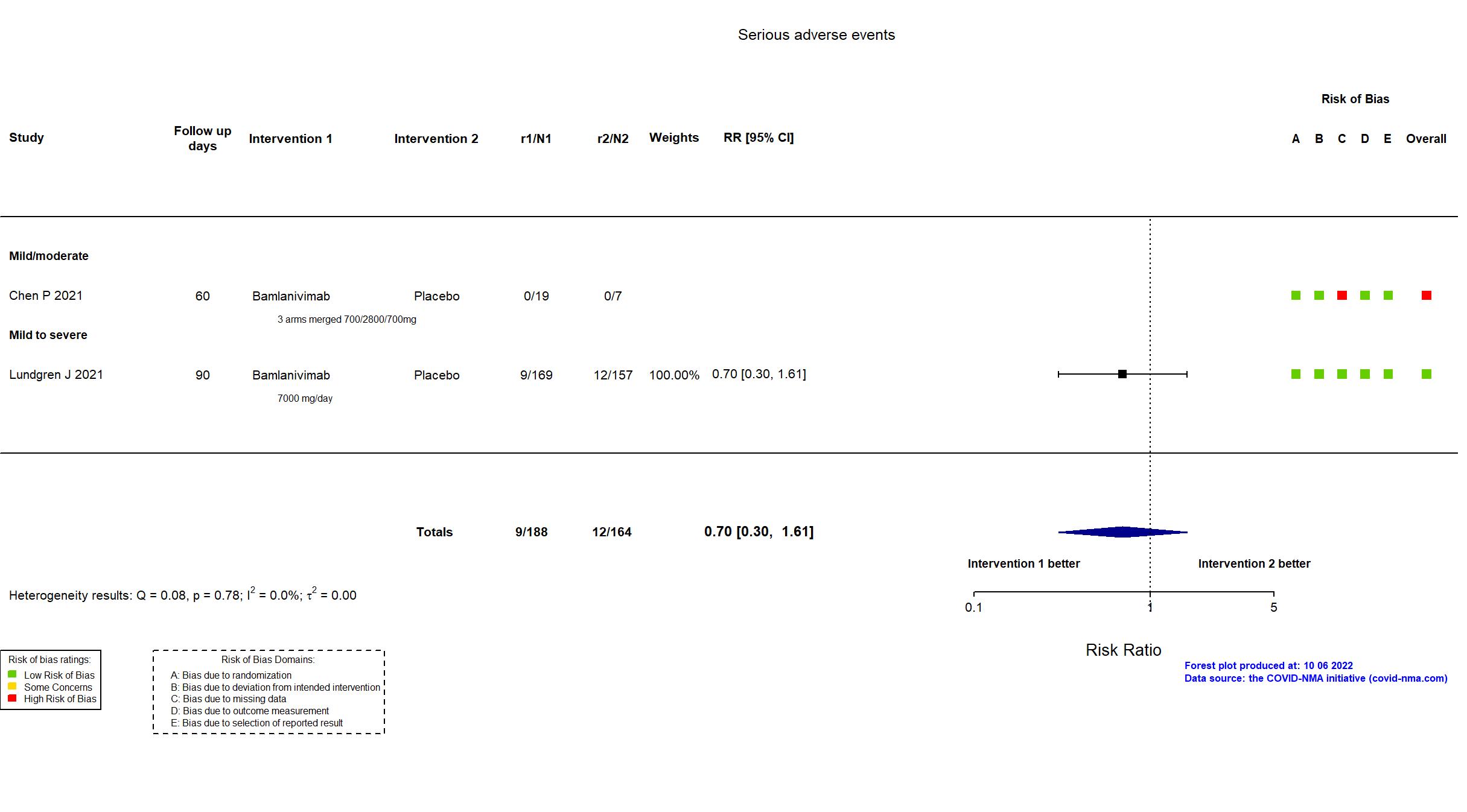
| In the register Number of Participants With One or More Serious Adverse Event(s) (SAEs) Considered by the Investigator to be Related to Study Drug Administration [ Time Frame: Baseline through Day 60 ] An SAE is any adverse event that results in death, persistent or significant disability/incapacity, or drug dependency/abuse; is life-threatening, an important medical event, or a congenital anomaly/birth defect; or requires or prolongs hospitalization. The number of participants with 1 or more SAEs considered by the investigator to be related to study drug administration is reported. A summary of SAEs and other non-serious adverse events (AEs), regardless of causality, were reported in the Reported Adverse Events module. | |
| In the report Safety and tolerability, including adverse events (AEs), serious adverse events (SAEs), and discontinuations due to AEs | |
| Documents avalaible |
Protocol Yes. In English Statistical plan Yes Data-sharing willing stated in the publication: Yes |
| Risk of bias Overall The overall risk of bias reported in the table corresponds to the highest risk of bias for the outcomes assessed for the systematic review |
High |
| General comment | This is a first-in-human study. In addition to the published article and its supplement, the protocol, SAP and study registry were used in data extraction and risk of bias assessment. There is no change from the trial registration in the intervention and control treatments. The registry primary outcome does not fully reflect the reported primary outcome. Sample size was very small, with n=6 analyzed per arm. The study (n=26) did not achieve the target sample size specified in the trial registry (n=40). |
Trial NCT04501978
Publication ACTIV-3/TICO - Lundgren J, J Ann Intern Med (2021) (published paper)
Dates: 2020-08-05 to 2020-10-13
Funding: Mixed (U.S. Operation Warp Speed; National Institute of Allergy & Infectious Diseases; Leidos Biomedical Research; National Heart, Lung & Blood Institute; Research Triangle Institute; U.S. Dept of Veterans Affairs; Denmark, Aus)
Conflict of interest: Yes
| Methods | |
| RCT Blinding: quadruple blinding | |
| Location :
Multicenter / Denmark, Singapore, USA Follow-up duration (days): 90 | |
| Inclusion criteria |
|
| Exclusion criteria |
|
| Interventions | |
| Treatment
Bamlanivimab 7000 mg IV infusion once-off |
|
| Control
Placebo | |
| Participants | |
| Randomized participants : Bamlanivimab=169 Placebo=157 | |
| Characteristics of participants N= 326 Mean age : NR 177 males Severity : Mild: n=86 / Moderate: n=* / Severe: n=* Critical: n=0 | |
| Primary outcome | |
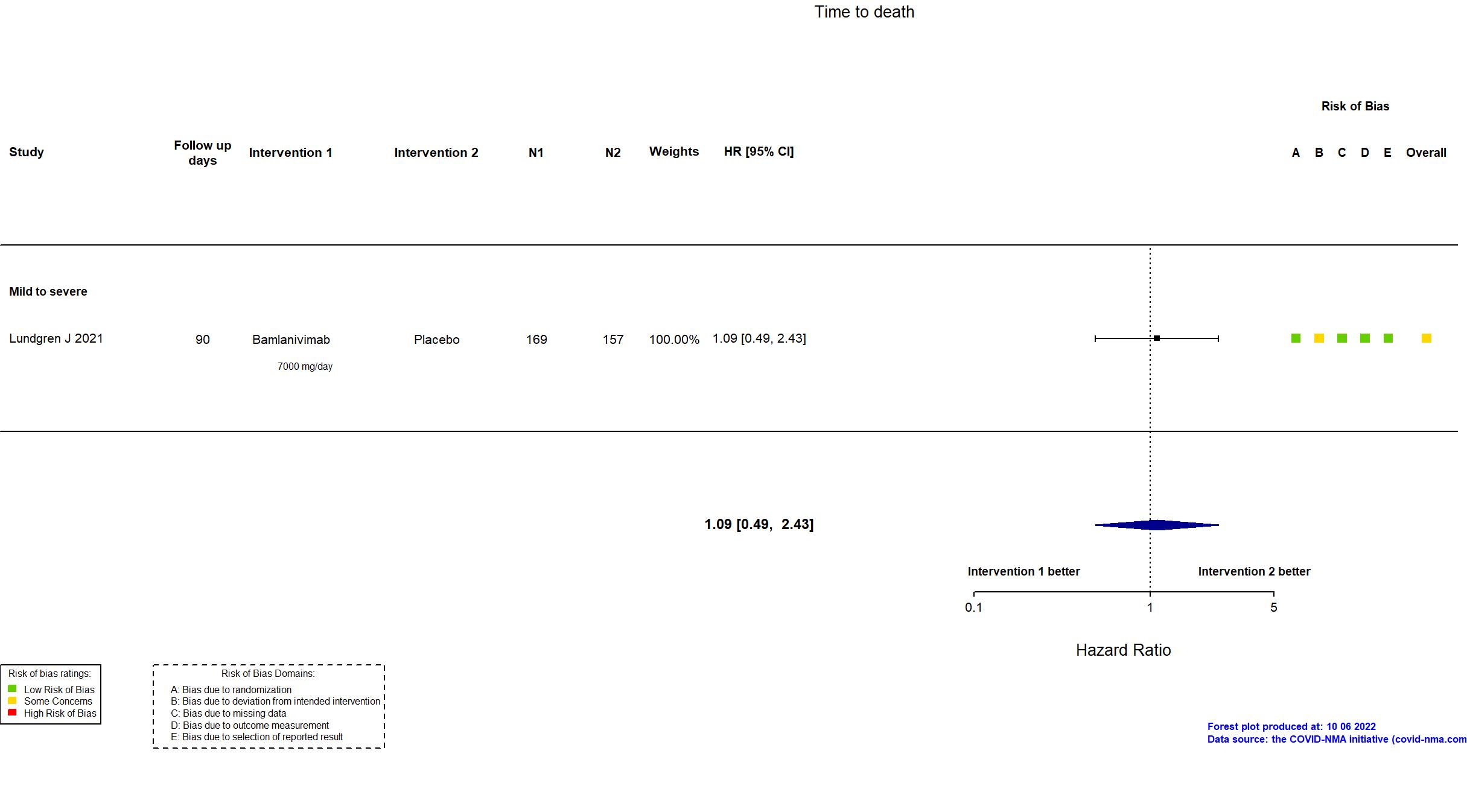
| In the register Pulmonary ordinal outcome [ Time Frame: Day 5 ] Oxygen requirements measured by 7 categories (1 = least severe, 7 = most severe). The participant's highest (i.e. most severe) observed score is used ; Pulmonary+ ordinal outcome [ Time Frame: Day 5 ] Extrapulmonary complications and respiratory dysfunction measured by 7 categories (1= least severe, 7 = most severe). The participant's highest (i.e. most severe) observed score is used. Time from randomization to sustained recovery [Time Frame: Up to Day 90 ] Sustained recovery defined as being discharged from the index hospitalization, followed by being alive and home for 14 consecutive days prior to Day 90. | |
| In the report Two ordinal outcomes termed “pulmonary” and “pulmonary- plus” assessed at day 5 after infusion were used to assess futility after at least 300 patients. Time to a sustained recovery, which was defined as hospital discharge to home and remaining at home for at least 14 days. | |
| Documents avalaible |
Protocol Yes. In English Statistical plan Yes Data-sharing willing stated in the publication: Yes |
| Risk of bias Overall The overall risk of bias reported in the table corresponds to the highest risk of bias for the outcomes assessed for the systematic review |
Some concerns |
| General comment |
In addition to the published article, the trial registry, study protocol, statistical analysis plan and supplementary materials were used in data extraction and assessment of risk of bias. There were no substantive differences between the published article and the trial registry, study protocol and statistical analysis plan. The trial did not achieve its pre-stated sample size as it was terminated for futility on the recommendation of the data and safety monitoring board.
Quote: "In order to respond to pandemic dynamics, this platform protocol incorporates an early futility and safety evaluation after the enrollment of 300 patients (stage 1). Stage 1 is then followed by enrollment to the full sample size (stage 2) for agents that pass the initial futility and safety assessment." "The analysis data set was locked on November 6, 2020, and includes deaths, serious adverse events, organfailure events, and hospital discharges that occurred up to October 26." Chance imbalances in illness severity at baseline were detected and reported by the authors, but adjusted analyses did not suggest benefit for LY-CoV555 in this patient population. This trial was updated on July 29th, 2021 with data from a preprint article reporting final results. This study was updated on January 20th, 2022 with data from the published article reporting on final results |